Get the Facts
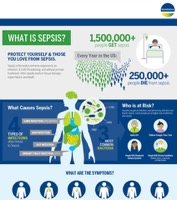
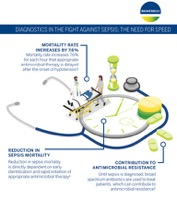
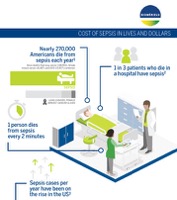
Sepsis occurs when the body's immune system mounts a dysregulated response in defense against a severe infection. This systemic inflammatory reaction can cause significant complications, including organ dysfunction and organ failure, potentially leading to long-term disability or patient death. The number of deaths caused by sepsis is constantly increasing due to the aging of the population and antimicrobial resistance. Because sepsis can be caused by virtually any pathogen, the very best hope for sepsis patients is early detection.
Diagnostics and Sepsis Care
There is no singular solution for the diagnosis of sepsis because underlying infections can be caused by many different pathogens. Early diagnostic intelligence helps shorten the time to treatment and allows hospitals to optimize patient care with the right antibiotic therapy at the right time. This is particularly important because infections are increasingly resistant to treatment. Additionally, ongoing surveillance capabilities support the timely discontinuation of treatment, which help minimize the risks and impact of antibiotic overuse.
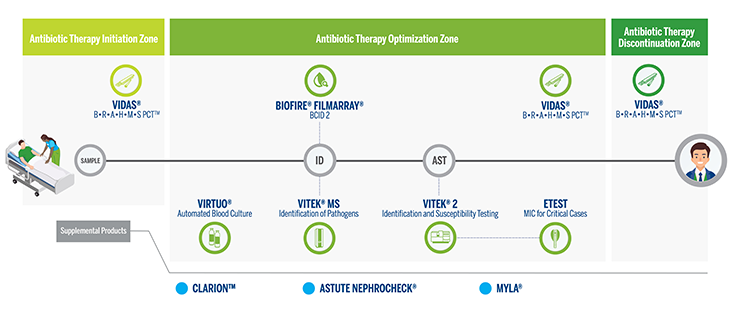
Diagnostics can inform sepsis care at every stage--from initial presentation and risk assessment, to pathogen detection, identification, susceptibility testing, monitoring patient progress, and safe antibiotic discontinuation.
Identifying sepsis risk as quickly as possible is critical for immediate treatment.
Sepsis may be diagnosed too late because the clinical symptoms, including high fever and increased pulse or respiratory rate, are non-specific. In this race against time, measuring procalcitonin levels with VIDAS® B·R·A·H·M·S PCT™ gives an early indication of severe bacterial infection in just 20 minutes. Physicians can use this information in making the decision to administer empiric antibiotic treatment, helping reduce the risk of injury and fatality.
Detect and identify pathogens and susceptibility as early as possible.
After initial risk assessment and administration of empiric therapy, pathogen detection, identification, and susceptibility testing provide critical information about whether the initial therapy needs to be adjusted. This is especially important because a patient may have an infection that is resistant to certain antibiotics, and because it allows physicians to optimize therapy.
Monitoring for complications and patient progress are critical for optimizing outcomes.
To optimize patient outcomes, physicians need to monitor patients for complications and for response to treatment. Diagnostics provide valuable information for critical points in the decision-making process, including assessing risk of kidney injury, which is a common complication of sepsis. Diagnostics can also help optimize treatment by providing information about patient progress and response to antibiotics.
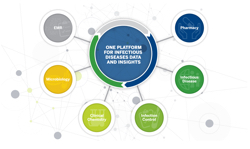
Advanced data and analytics are a weapon in the fight to eliminate sepsis.
To support healthcare systems in their efforts of systematically screening and understanding of sepsis, new analytic platforms are available to enhance data application, collaborative communication and decision making.
Integrating Sepsis Care and Antimicrobial Stewardship
 Antimicrobial resistance threatens effective sepsis care in a variety of ways. Every hour counts with sepsis patients, so there is a strong drive to initiate antibiotic treatment as quickly as possible. But, because sepsis is a result of an underlying infection which may or may not be resistant to treatment, we must address antimicrobial stewardship as part of sepsis care management. Additionally, Clostridium difficile (C. difficile) infections, which often result from antibiotic exposure, call for more effective efforts to reduce the unnecessary and prolonged use of antibiotics in self-limiting non-bacterial infections and in resolving bacterial infections.
Antimicrobial resistance threatens effective sepsis care in a variety of ways. Every hour counts with sepsis patients, so there is a strong drive to initiate antibiotic treatment as quickly as possible. But, because sepsis is a result of an underlying infection which may or may not be resistant to treatment, we must address antimicrobial stewardship as part of sepsis care management. Additionally, Clostridium difficile (C. difficile) infections, which often result from antibiotic exposure, call for more effective efforts to reduce the unnecessary and prolonged use of antibiotics in self-limiting non-bacterial infections and in resolving bacterial infections.
Fast and actionable diagnostics remain a key component to antimicrobial stewardship efforts, from the onset of suspected sepsis to pathogen identification, antibiotic susceptibility testing, patient monitoring, and antibiotic discontinuation. bioMérieux’s sepsis solutions can help stewardship teams improve antimicrobial prescribing practices and patient outcomes.
Sepsis and Acute Kidney Injury
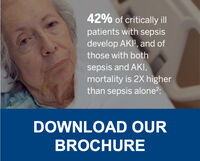 Sepsis is a risk factor for developing acute kidney injury (AKI), and having AKI puts patients at higher risk of sepsis. Early detection of AKI in sepsis patients is critical for delivering optimal treatment and can be supported by the use of biomarkers. Similarly, early diagnosis of AKI during the onset of an infection could impact the severity of sepsis in individual patients.
Sepsis is a risk factor for developing acute kidney injury (AKI), and having AKI puts patients at higher risk of sepsis. Early detection of AKI in sepsis patients is critical for delivering optimal treatment and can be supported by the use of biomarkers. Similarly, early diagnosis of AKI during the onset of an infection could impact the severity of sepsis in individual patients.
bioMérieux supports reframing the challenges that physicians face in sepsis care and the importance of addressing issues such as AMR and AKI concurrently. Through industry partnerships, ongoing advocacy for diagnostics, and development of educational resources for professionals and patients, bioMérieux continues to lead the way with sepsis care solutions.
Sepsis Resources
Sepsis Training & Education Opportunities
External Partner Resources
bioMérieux, Inc. is a proud sponsor of the Sepsis Alliance, a leading nonprofit patient advocacy organization in North America. Sepsis Alliance's mission is to save lives by raising awareness of sepsis as a medical emergency. We invite you to view their collection of educational resources and information guides.
bioMérieux is a proud supporter of the Global Sepsis Alliance, a nonprofit charity organization with the mission to provide global leadership to reduce the worldwide burden of sepsis. We encourage you to visit the 2020 World Sepsis Day Toolkit that includes timely information and educational resources.
References
- Rudd K, Johnson S, Agesa K, Shackelford K, Tsoi D, Kievlan D, et al. Global, regional, and national sepsis incidence and mortality, 1990–2017: analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study. The Lancet. 2020;395(10219):200-211. doi:org/10.1016/S0140-6736(19)32989-7.
- Rhee C, Jones TM, Hamad Y, et al. Prevalence, Underlying Causes, and Preventability of Sepsis-Associated Mortality in US Acute Care Hospitals. JAMA Network Open. 2019;2(2):e187571. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2018.7571
- bioMérieux. Sepsis. bioMérieux Global Website. Available at: https://www.biomerieux.com/en/sepsis. Accessed Aug 28, 2020.
PRN 057174 Rev 0.1B